Address
Floor 3, Building B, Honghua Science And Technology Innovation Park,
Longhua District, Shenzhen
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 9PM
Weekend: 10AM - 6PM
Address
Floor 3, Building B, Honghua Science And Technology Innovation Park,
Longhua District, Shenzhen
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 9AM - 9PM
Weekend: 10AM - 6PM

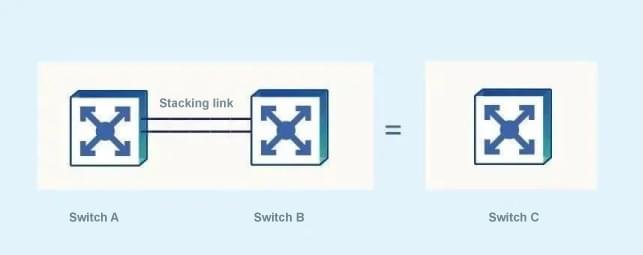
Stacking refers to connecting multiple switches that support stacking features through stacking cables, and logically virtualize them into a switching device, which participates in data forwarding as a whole. Stacking is a horizontal virtualization technology widely used at present, which has the functions of improving reliability, expanding the number of ports, increasing bandwidth, and simplifying networking.
Traditional campus networks use equipment and link redundancy to ensure high reliability, but their link utilization is low and network maintenance costs are high. Stacking technology virtualizes multiple switches into one switch to simplify network deployment and reduce network maintenance workload. Stacking has many advantages:
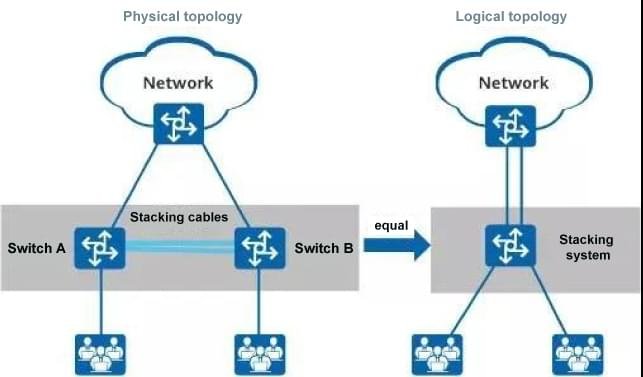
A redundant backup is formed between multiple member switches of the stacking system. As shown in the figure below, Switch A and Switch B form a stacking system, and Switch A and Switch B back up each other. When Switch A fails, Switch B can take over Switch A to ensure the normal operation of the system. In addition, the stacking system supports link aggregation across devices and can also implement link redundancy backup.
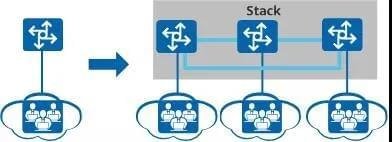
As shown in the figure below, when the number of connected users increases to the extent that the port density of the original switch cannot meet the access requirements,new switches can be added to form a stacking system with the original switch to expand the number of ports.
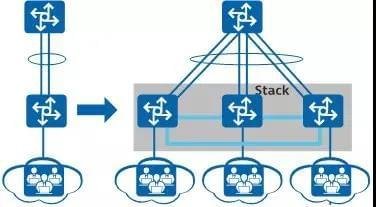
As shown in the figure below, when you need to increase the upstream bandwidth of the switch, you can add a new switch and the original switch to form a stacking system, and configure multiple physical links of the member switches into an aggregation group to increase the upstream bandwidth of the switch.
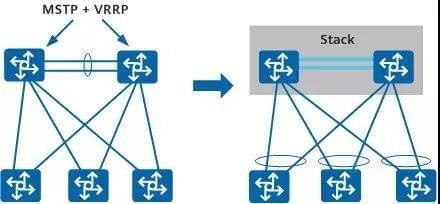
As shown in the figure below, multiple devices in the network form a stack, which is virtualized into a single logical device. The simplified networking no longer needs to use MSTP and other ring-breaking protocols, which simplifies the network configuration. At the same time, it relies on cross-device link aggregation to achieve rapid switching when a single device fails and improve reliability.
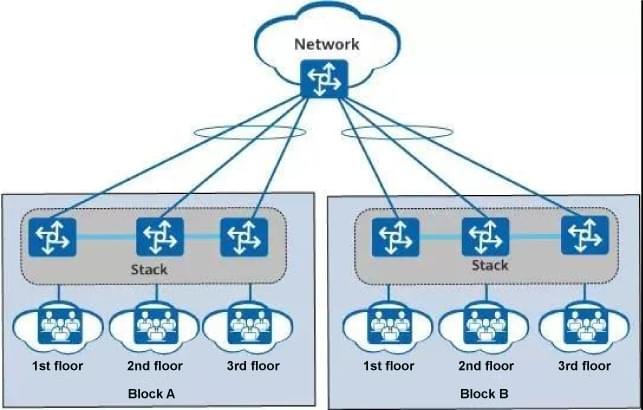
As shown in the figure below, users on each floor connect to the external network through corridor switches. Now the corridor switches that are far apart are connected to form a stack, which is equivalent to only one access device in each building, and the network structure becomes simpler . Each building has multiple links to reach the core network, and the network becomes more robust and reliable. The configuration of multiple corridor switches is simplified into the configuration of a stacking system, which reduces management and maintenance costs.
Before introducing how the stack is established, let’s first introduce the related concepts used in the process of stack establishment.
All single switches in a stack system are called member switches, and can be divided into three roles according to their different functions:
The master switch, standby switch and slave switch can all forward business traffic. Adding, removing, or replacing stack member switches may cause changes in the roles of stack members.
The stack ID is used to identify the stack member switch and is the slot ID of the member switch. Each stack member switch has a unique stack ID in the stack system.
The stack priority is an attribute of member switches, which is mainly used to determine the role of member switches in the role election process. The larger the priority value, the higher the priority, and the higher the priority, the greater the possibility of being elected as the master switch.
The process of stack establishment includes the following four stages:
Comments are closed.
The stack priority is an attribute of member switches, which is mainly used to determine the role of member switches in the role election process